Accessibility Resources
Practical Tips For Making Websites Accessible In California
Website accessibility is not a side task anymore. It is part of good web design, good customer service, and good risk management. In California, it matters even more because businesses are expected to give people with disabilities equal access to online services. Federal ADA guidance says businesses open to the public must make sure their online goods, services, and programs are accessible, and digital accessibility compliance California is an important part of meeting these expectations, while California state accessibility materials point to WCAG 2.2 Level AA and the Unruh Civil Rights Act as key standards in this space.
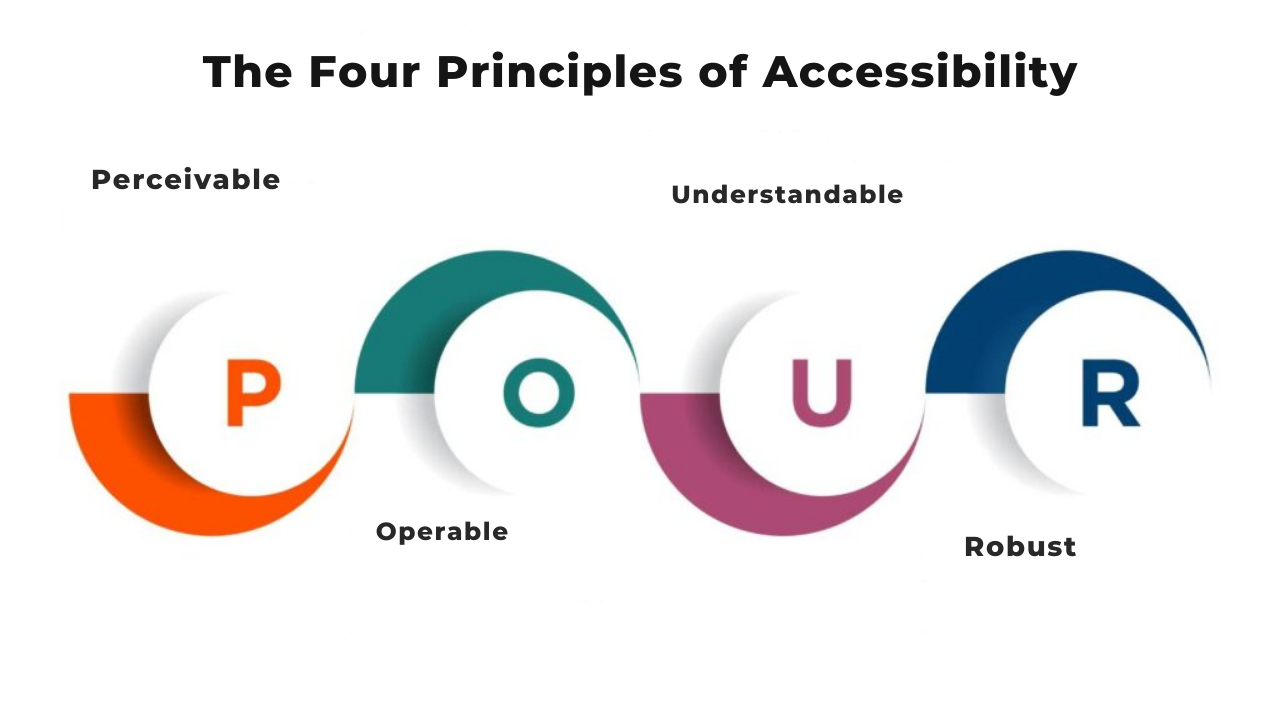
That can sound complicated at first. It does not have to be. The best way to think about creating accessible websites is simple: can real people use your site with a keyboard, screen reader, captions, clear text, and enough visual contrast? If the answer is no, there is work to do. WCAG 2.2 is built around four main ideas: content should be perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust.
Digital Accessibility Compliance California: Full Guide 2026
Digital access is now a basic part of doing business and serving the public. People use websites, mobile apps, online forms, PDFs, payment portals, and service dashboards every day. If those tools are hard to use with a screen reader, keyboard, captions, Zoom, or voice control, many users are blocked from equal access.
That is why this topic matters in 2026. Digital Accessibility Compliance California is becoming increasingly important because California has state rules for public entities, and federal disability law also affects digital access. At the same time, businesses in California face real legal risk when their digital services create barriers for people with disabilities.
So, a clear digital accessibility compliance guide for California businesses and public teams to follow is no longer optional. It is part of basic risk control and good service design.
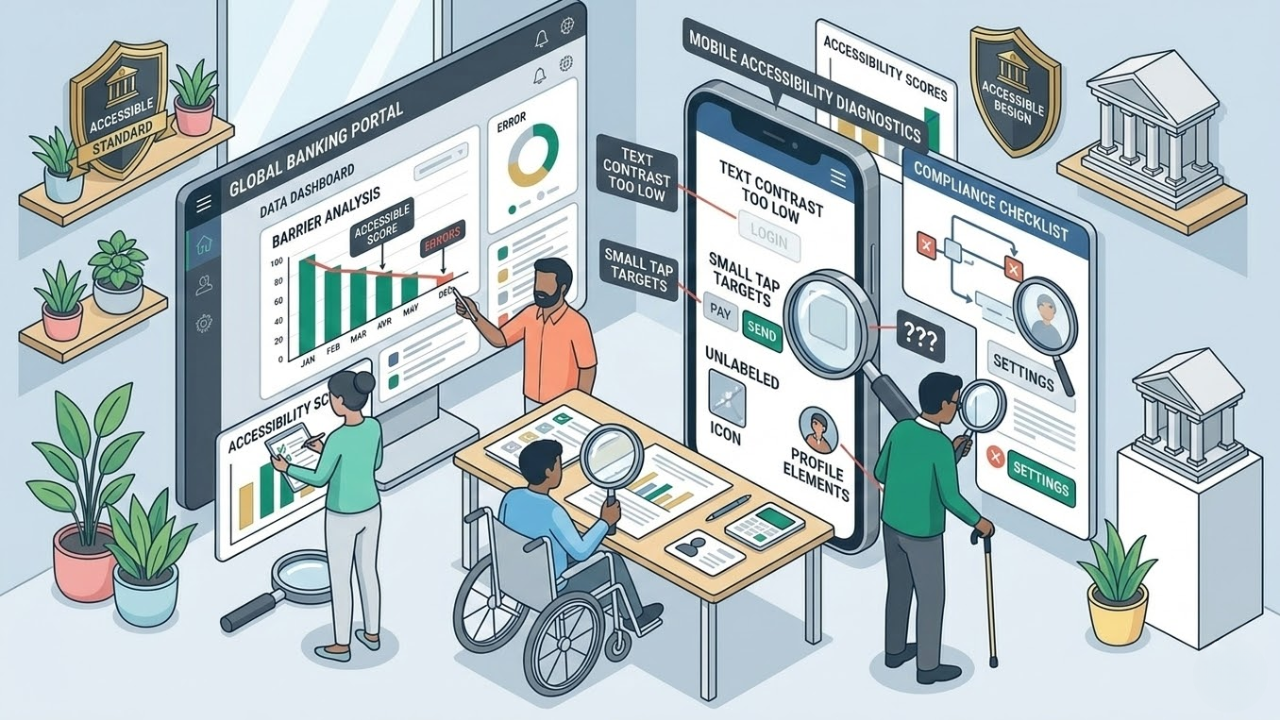
Common Accessibility Mistakes In Mobile Banking User Experience
Mobile banking should feel simple. A person should be able to check a balance, pay a bill, review a transaction, or lock a card without confusion. But many banking apps still create barriers that make basic tasks harder than they need to be. This is why the idea of accessible banking has become more important for financial institutions that want their apps to work well for everyone.
Some of those barriers are obvious. The buttons are too small. Text is too light. Labels are missing. Others are harder to notice. A timeout ends a session too fast. A screen reader reads a chart with no useful meaning. A login step depends too much on memory or drag-and-drop actions. These are not small details.
In banking, small mistakes can block access to funds, cause stress, and erode people's trust in the app. WCAG 2.2 now includes guidance on topics such as target size and accessible authentication, and the W3C has also published guidance on how WCAG 2.2 applies to mobile apps.
Hidden Accessibility Gaps That Impact Banking Websites
Online banking is now the main way people manage money. Many people no longer visit branches. They check balances on a phone. They pay bills from a laptop. They send money to their families in minutes. This convenience is helpful. But it also brings a new problem. If a banking website is hard to use, some customers get blocked from basic financial tasks.
Many banks think their websites are accessible. They may run a quick scan. They may fix a few visible issues. They may add an accessibility tool. Then they assume the problem is solved. But real accessibility is not always obvious. A website can look fine and still be difficult for many users. The biggest issues are often hidden inside forms, pop-ups, menus, and mobile screens. These are Hidden accessibility gaps in banking websites. They can quietly create real harm.
The Role of WCAG Guidelines in Online Banking Accessibility
Online banking is now part of everyday life. People check balances in the morning. They pay bills at night. They transfer money while traveling. Many customers depend fully on websites and mobile apps to manage their finances. Because of this, online banking must work for everyone.
Some users cannot see clearly. Some cannot hear audio. Some cannot use a mouse. Others may process information more slowly. If online banking does not support these needs, it creates barriers. Those barriers can stop people from accessing their own money.
This is where WCAG guidelines become important. WCAG gives clear rules for building websites that everyone can use. In this article, you will understand what WCAG is, why it matters in banking, and how it shapes Online banking accessibility features in real ways.
Top 10 Tips for Improving Online Banking Accessibility Features
Online banking is where real life happens now. People pay rent, send money to family, check refunds, and track spending from a phone screen. For many customers, the website or app is the bank. That is why accessibility cannot be “nice to have.” If someone cannot log in, read a statement, or confirm a transfer, the service is not doing its job.
Accessibility means this: the site works for people with different needs and different abilities. Some users rely on screen readers. Some can only use a keyboard. Some need larger text, clearer colors, or simpler steps. When those needs are ignored, customers get stuck. When they are supported, customers feel in control.
Below are ten practical tips that make a real difference. They are written for teams who want clear actions, not vague advice. The focus is on real-world online banking accessibility tasks, such as signing in, paying bills, transferring funds, and reviewing account activity.
A Complete Guide to Banking Website Accessibility!
Banking is part of everyday life. People check balances, pay bills, transfer money, and apply for loans online. Many customers rarely visit a physical branch. They depend on websites and mobile apps to manage their finances. Because of this, digital access must work for everyone. If a banking website is hard to use for someone with a disability, that person may lose access to essential services. That is not acceptable.
This complete guide to banking accessibility explains what accessibility means in simple terms. It also explains why it matters and how banks can improve their digital platforms step by step. The goal is clear. Every customer should be able to use online banking without barriers.
The Digital Accessibility Gap In Education Is Growing Fast
Education has moved online faster than schools could plan for. raising new questions about the accessibility of education. Classes now depend on websites, learning platforms, PDFs, videos, and apps. That shift helps many students, but it also leaves others behind.
When a student cannot read a worksheet because it is an image, that student is blocked. When a video has no captions, that student loses information. When a quiz does not work with a keyboard, the student cannot finish the test.
These are not rare edge cases. They are everyday barriers that add up fast.
One reason this is getting worse is that the web itself is still full of accessibility failures. In WebAIM’s Million report, 95.9% of the top one million home pages had detectable WCAG failures. That tells us something important: if the broader web struggles, education systems that rely on the same tools and habits will struggle too.
Benefits Of Website Accessibility For School Websites
School websites are no longer just online notice boards. They are where families enroll students, check calendars, read updates, download forms, and find support services. They are also where students access learning links, announcements, and resources that shape their day-to-day experience.
Because of this, a school website has to work for everyone. That includes people who use screen readers, people who cannot use a mouse, people who need captions, and people who need clear layouts to understand information without stress.
Website accessibility is the practice of ensuring your online content can be used by as many people as possible.
This article explains the real, practical benefits of Digital Accessibility in Education websites. It also describes how accessibility connects to legal expectations, common barriers, and simple improvements that make a big difference.
Digital Accessibility In Education And WCAG Compliance
Digital learning has become normal in schools, colleges, and universities. Students attend classes online, submit assignments through portals, watch recorded lectures, and take assessments inside learning systems. Even parents and staff depend on online tools for communication, enrollment, scheduling, payments, and support.
But here is the truth: digital education is only effective when everyone can use it. If a student cannot read a PDF with a screen reader, cannot navigate a portal with a keyboard, or cannot understand a video without captions, the learning experience becomes unfair and stressful. This is precisely why digital accessibility matters in education.
Digital accessibility means that online learning content and tools are designed so that people with different abilities can use them without barriers. It is not just a technical requirement. It is part of equal access, inclusive learning, and good educational design.
Key Accessibility Features Every Education Website Needs
Education websites are no longer just “nice to have” tools. They are where people learn, enroll, pay fees, find help, and stay informed.
And many people depend on them in ways we do not always see.
In the United States, 7.5 million students ages 3–21 were served under IDEA in the 2022–23 school year.
That is one reason accessibility in education matters so much. If a website blocks someone from reading a lesson, filling a form, or finding support, it can block real learning.
This article explains what to build and what to fix to improve accessibility.
Importance of Website Accessibility in Education: A Full Guide
Website accessibility in education means everyone can use the school or college website, regardless of their abilities or the device they use. A student using a screen reader should be able to access course materials just as easily as a student using a mouse. A parent on an old phone should be able to check their child's grades without barriers.
This matters more in educational settings than almost anywhere else. Schools and colleges serve entire communities with vastly different abilities, devices, and technical skills. When an educational website isn't accessible, it blocks students from learning and families from staying informed.
This blog focuses on the real value and impact of accessibility. You'll understand why accessibility in education goes far beyond legal compliance and how it creates better experiences for everyone in your educational community.
ADA Compliance Checklist for Ecommerce Businesses
Your online store needs to work for everyone. That includes the millions of people with disabilities who shop online every day.
ADA compliance for ecommerce isn't optional anymore. It's a legal requirement. More importantly, it's the right thing to do. When your website is accessible, you open your business to a much larger customer base.
The problem is that most ecommerce sites weren't built with accessibility in mind. Buttons that screen readers can't identify. Images without descriptions. Checkout processes that keyboard users can't complete. These barriers lock out potential customers and expose you to lawsuits.
Key Principles of Ecommerce Website Accessibility
Ecommerce websites are an integral part of our daily lives. Customers use them to purchase clothing and tickets, buy food items, and organize their essentials. However, not all people experience these sites in the exact way. For many, obstacles such as poor navigation, unclear text, or confusing checkout flow make shopping online difficult and sometimes impossible.
This is the point at which Ecommerce accessibility principles come into play. These guidelines help ensure that online stores are accessible for everyone, even those who have hearing, visual, and motor impairments. When accessibility is integrated into an online store, it improves accessibility for all customers, not only disabled people.
Top 7 Web Accessibility Ecommerce Features You Must Add
Most online stores are built to look good. But shopping is not only about looks. It is about getting the job done. A shopper should be able to browse, compare, and check out without getting stuck.
That is what accessibility helps you achieve. Ecommerce accessibility is often explained as “support for people with disabilities.”
In this blog, you will learn seven accessibility features for websites that make an online store easier to use.
They also help reduce common drop-offs during browsing and checkout
How Ecommerce Accessibility Can Improve User Experience
When someone shops online, they want a smooth path. They want to find a product, understand it, and buy it without friction. Accessibility helps make that path smoother.
It removes barriers that block real people from using your store.
Web accessibility means your site is designed so people with disabilities can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with it. But here is the crucial part. Many accessibility improvements also make sites easier for everyone, including people in bright sunlight, on small screens, or dealing with slow connections.
Ecommerce Website Accessibility: What Every Retailer Must Know
Ecommerce accessibility means your online store works for people with different abilities. It means shoppers can browse, read, click, and pay without hitting barriers.
This is not a “nice-to-have” detail. It affects real people and real revenue. A shopper may use a screen reader. Another may not use a mouse. Someone else may need bigger text, clearer buttons, or captions. If your store blocks them, you lose a sale. And they may never come back.
This blog will help you learn what accessibility looks like in a real store, what standards people use, what legal updates are worth knowing, and what to fix first.
Web Accessibility Basics: The Four Foundational Principles
You've probably heard that websites should be accessible. But what does that actually mean? Where do you even start?
The answer is simpler than you think. Web accessibility boils down to four basic ideas. Get these right, and you're well on your way to building websites that work for everyone.
These four principles come from WCAG, which stands for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. They form the foundation of everything else in web accessibility. Think of them as your starting point for understanding accessibility principles and how they shape the web.
This blog will discuss what each principle means and why it matters.
Skip to Main Content Links: A Simple Step Toward Better Accessibility
When you open a website, you probably scroll or click without thinking much about it. You see the menu, you ignore it, and you go straight to what you want, so it feels easy.
But that is not how everyone experiences a website.
Some people do not use a mouse at all. They move through a page using a keyboard. Some people cannot see the screen and rely on a screen reader to read the page out loud. For them, a website feels very different. which is why regular accessibility monitoring is important to understand how real users interact with your content.
Every menu item, every link, every button is reached one at a time.
If a page has an extended header with many links, they must go through all of it before they reach the actual content.
Mobile Accessibility: Practical Techniques for Designers and Developers
Think about how often we use our phones every day. We order food, read news, book rides, shop, and chat, all from small screens. Now imagine trying to do all of that if you can’t see clearly, can’t tap tiny buttons, or rely on a screen reader to understand what’s on the screen.
That’s where mobile accessibility comes in.
Mobile accessibility means making sure your mobile website or app works for everyone, including people with disabilities. It’s not about doing something extra or fancy. It’s about designing and building things in a way that doesn’t leave people out.
The good news? When you design for accessibility, you usually end up creating a better experience for all users — not just those with disabilities.